Introduction to adaptive models reporting in 7.3 and 7.4
Adaptive models belong to the self-learning aspect of decision management in Pega Platform™. They are predictive models that learn about your customers' behavior to make relevant decisions. For example, when a customer accepts one of your offers, the likelihood of customers with a similar profile accepting this offer increases. Additionally, future customers can then receive a more personalized and relevant offer. The Adaptive Decision Manager (ADM) service builds the models based on the customer and contextual data (predictors) as well as the responses it receives. The models are updated regularly, and in this way the strategy that references the models adapts automatically to changes in behavior that occur over time.
Use the Adaptive Models Management landing page, the Analytics Center portal, and default reports in Pega Platform to better understand adaptive models and monitor their performance.
Prerequisites
Before you read about adaptive models reporting, you can learn about adaptive models in decision strategies from the following Pega Academy courses:
- How to design a decision strategy
- Decision strategy execution
- Using decision analytics in a decision strategy
Adaptive models reporting
You access reports for adaptive models on the Adaptive Models Management landing page to view the performance of your models and their predictors. Information that you can obtain from the Adaptive Models Management landing page is important for business users (business scientists, data scientists, and business intelligence specialists) and for strategy designers, because this information can result in changes to the decision strategy and adaptive models. For example, you can identify poorly performing models, check the performance of newly introduced propositions, and change the prioritization in the decision strategy.
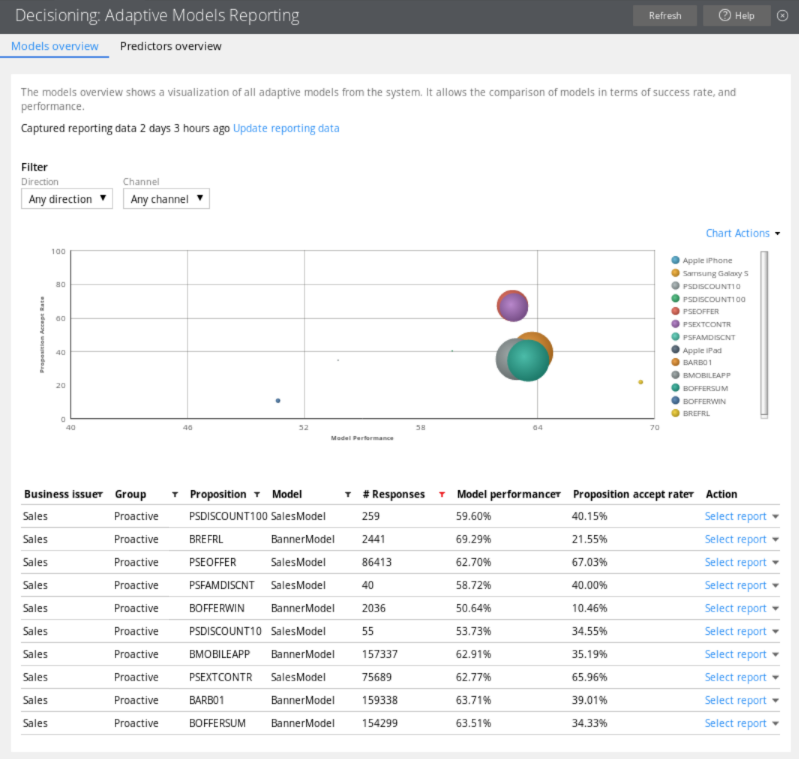
Adaptive models report
In the bubble chart, each circle represents one model for a specific proposition. The size of a circle represents the number of responses (positive and negative). By placing the mouse cursor on the circle, you can view the number of positives and negatives, and the number of times that the proposition was presented to the customer. The Performance axis indicates the accuracy of the outcome prediction. The model performance is expressed in Area Under the Curve (AUC), which has a range between 50 and 100. High AUC means that the model is good at predicting the outcome, low AUC means that the outcome is not predicted accurately. The Success Rate axis indicates the proposition accept rate expressed in percentages. It is the number of positive responses divided by the total number of responses. When customers receive propositions for which they have a high propensity score, the success rate of a model increases.
When to use adaptive models reporting
Use adaptive models reporting to:
Identify technical problems.
In the Models overview tab, look for adaptive models with an acceptance rate of zero. This means that the propositions for these models do not receive any positive responses, and you need to check their configurations. For more information, see Proposition Management landing page.
Identify propositions for which the model is not predictive.
In the Models overview tab, look for adaptive models with low performance; these are the models in the left side of the chart. Their performance can be increased when you add predictors that have not been considered in the adaptive model yet. For more information, see Predictors.
Identify propositions that have a low number of responses.
In the Models overview tab, look for adaptive models with a low number of responses; these models are represented by the small circles in the chart. You might want to investigate eligibility criteria in the decision strategy and change exclusion settings to increase the proposition's frequency. For more information, see the component categories in Completing the Strategy tab.
Identify propositions that are proposed so often that they dominate other propositions.
In the Models overview tab, look for adaptive models with a high number of responses; these models are represented by the big circles in the chart. A high number of responses might be fine from the business point of view. However, if necessary, you can adjust prioritization in the decision strategy to decrease the proposition's frequency. For more information, see Strategy components - Arbitration.
Identify propositions with a low success rate.
In the Models overview tab, look for adaptive models with a low success rate; these are the models that are close to the Performance axis. If the model performance is also low, you can try to offer the proposition to more relevant customers to increase the success rate. If the model performance is already high, the relevance to the customers is high, but the proposition is unattractive and you might want to dismiss it. For more information, see Proposition Management landing page.
Inspect an adaptive model.
When your model performs well you might want to share positive feedback with the business people in your organization. If your model performs badly, you need to adjust its settings. You can open the Model report to inspect your model when a new proposition has been introduced, a predictor has been added or removed, or the prioritization in the decision strategy has changed. In the Model report, you can view the active and inactive predictors, investigate the top predictors, or check the uplift among the top-scoring customers. You can also identify the leaking predictors and remove them. For more information, see Adaptive Model, Proposition Management landing page, and Completing the Strategy tab.
Inspect a predictor.
Check the details of a predictor when your predictor has a low performance. A possible cause can be too many missing values for the predictor. Look at the top predictors and in the bins that have a particularly high or low success rate. To inspect a predictor, open the Model report.
Identify predictors that are never used.
In the Predictors tab, look for a predictor that is never used. You might consider removing it, but make sure that there are no propositions for which this predictor could be relevant in the future. For more information, see Predictors.
To ensure the accuracy of your adaptive models, perform the following tasks regularly:
- Inspect predictors every two or three months.
- Check the performance of your model every two weeks.
- Check the success rate of your model every two weeks.
- Check the settings of your model in the Adaptive model rule instance every month.
