Understanding the Pega deployment architecture
Pega Platform is a distributed system that is deployed by using one or more tiers of Pega nodes, as well as external services. All the Pega nodes communicate with each other to form a Pega cluster. Nodes within the cluster communicate with the relational database to access rules and data. A load balancer or Kubernetes ingress connects to the exposed Pega nodes to allow user access to the cluster.
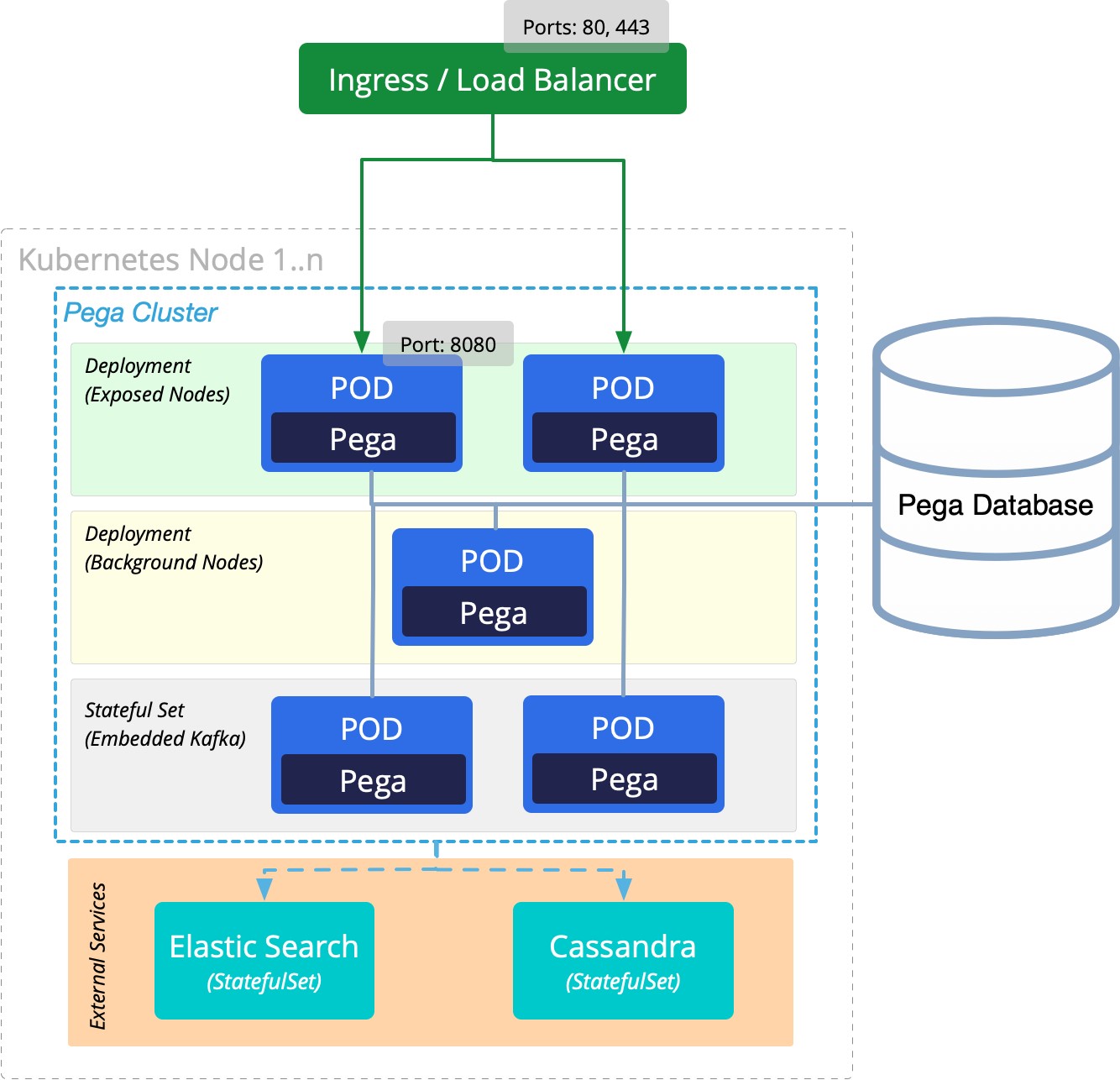
Pega applications and services are deployed by mapping Kubernetes objects with Pega Platform applications and services. Each tier of Pega nodes is built by using the same Pega Docker image, but they can be configured with unique parameters to allow for dedicated groups of nodes to be defined with unique node classifications, resource allocations, configurations, or scaling strategies.
By default, Pega deploys with three tiers of Pega nodes:
- Web – Includes nodes that are exposed to the load balancer using the “foreground” or “WebUser” type of node classification.
- Batch – Includes nodes that are not exposed by the load balancer, but are configured to handle background processing using the “background” type node classification. This tier handles workloads for BackgroundProcessing, ADM, Batch, RealTime, RTDG, Custom1, Custom2, Custom3, Custom4, Custom5, and BIX processing.
- Stream – Includes nodes that are configured to run an embedded Kafka service using the “stream” type node classification.
The default Pega Platform deployment in the Helm chart provides a base set of nodes in each tier. However, you can customize the Helm chart to meet your Pega application workload by specifying the number of tiers in your deployment. You can also use node classifications to specify to Pega that a specific node is intended for specific processing.
You can also customize the deployment of other services, including:
- Elasticsearch – Elasticsearch is required for your Pega application’s search capabilities. Default Pega Platform deployments include this search service by specifying the Pega-provided Elasticsearch Docker image that includes all required plug-ins. For Pega Infinity 8.6 and later, you can optimize Elasticsearch by processing it using SRS nodes. Pega also supports using your own pre-deployed Elasticsearch service. For more information, see Using full-text search based in Elasticsearch.
- Cassandra / DDS – A Cassandra deployment is required for applications that are built using the Decisioning and Marketing capabilities of Pega Platform. The included Helm chart will configure a standard Cassandra deployment using the publicly available image from DockerHub. If you do not want to deploy a new Cassandra instance, you can disable the setting; alternatively, to use your own pre-deployed Cassandra service, you can provide the location and security credentials of your service.
- Traefik – Use the Pega Helm chart to automatically deploy and configure Traefik as a load balancer. Pega Platform requires a load balancer or ingress for users and services to connect to the cluster. If you want to configure your own load balancer, you can disable Traefik deployment. You can find more details about load balancer compatibility, including session affinity requirements in the Platform Support Guide. For configuration options, see Choose the Kubernetes-based services for your deployment.
- EFK – Elasticsearch-Fluentd-Kibana is a standard logging stack that is provided as an example to help you get started. If your Kubernetes environment provides a logging stack, such as OpenShift or EKS, you can disable this deployment and use the native logging.
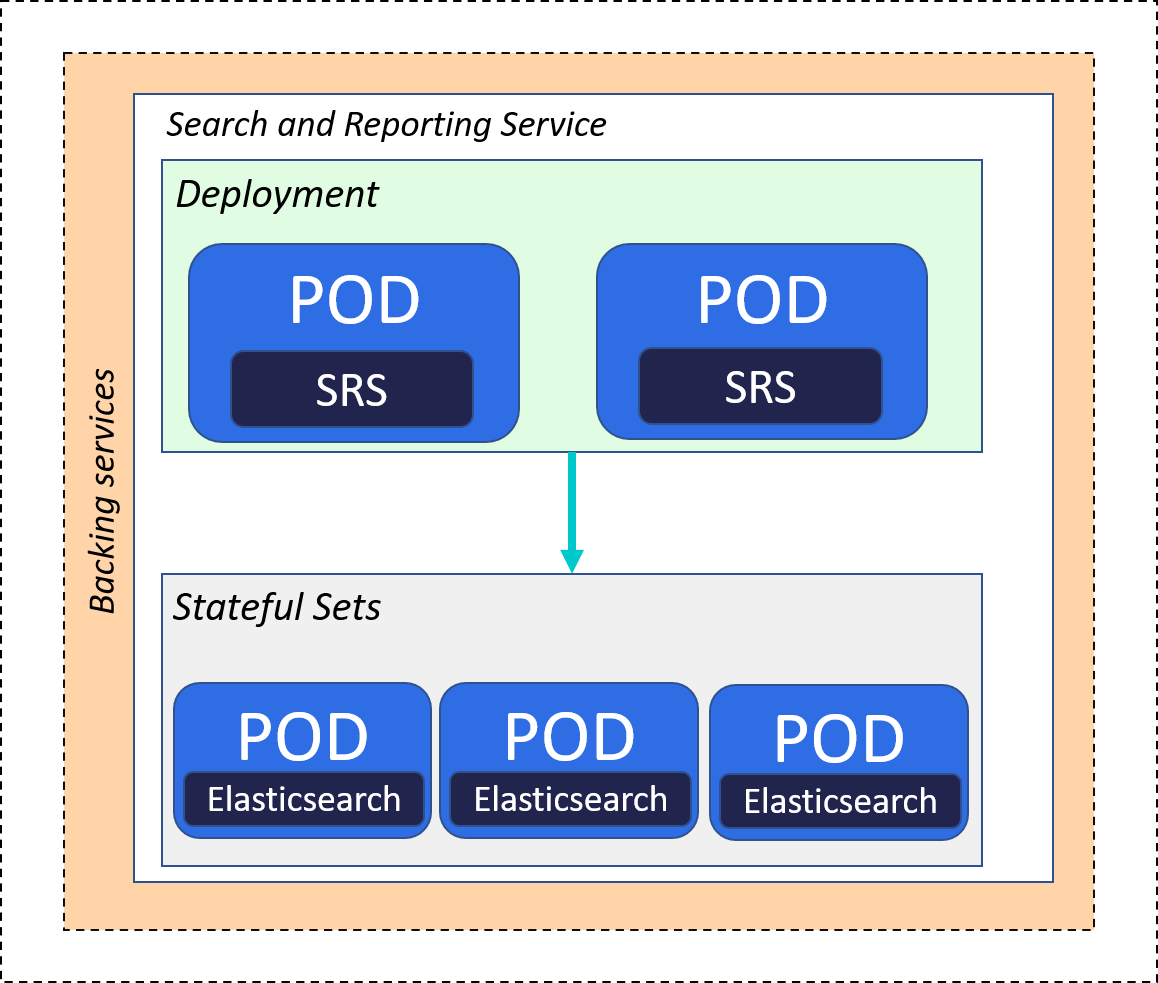
- Backing Services – The Pega Infinity backing service allows you to deploy the
latest generation of search and reporting capabilities to your Pega applications that run
independently on nodes provisioned exclusively to run these services. Deployments define
the node provisioning in your environment using the Search and Reporting Service (SRS)
subchart that you install in your deployment namespace. For Pega Infinity 8.6 and later,
the SRS can provide Elasticsearch for your Pega application. For more information, see
Configuring Pega backing services.
Kubernetes objects used to orchestrate a Pega Platform deployment
The orchestration of the Pega Platform uses the following Kubernetes objects:
Pod - A scalable unit of one or more containers with a specific configuration defined by a replica set. Pods are configured to use one of the Pega-provided Docker images which are detailed throughout this documentation, or a publicly available image in the case of some dependent services. Pega provides a Docker image for Web, Batch, and Stream Pega node types, and Docker images that support clusters running either an external search service or an SRS cluster.
The Pega web and optional stream nodes are associated with an ingress and require external network configuration to allow user access. In particular, the Pega web nodes allow user access to Pega Platform and all Pega applications installed. For DNS host name requirements, see Preparing your environment to deploy Pega Platform.
- Service - Defines a logical set of pods and a policy by which to access them. A deployment includes a definition of how services are exposed internally to other Kubernetes- managed resources or externally.
- ConfigMap - Manages configuration data that is injected into a container. You can use this object for XML-based configuration such as the Pega prconfig.xml file.
- Ingress - Manages external access to the services in a cluster to provide load balancing of the nodes across the deployment.
For information about these objects and managing your Docker images for pod configurations, see the Kubernetes documentation.
To support Kubernetes deployments of the Pega application and its required services, Pega provides configuration definitions for multiple tiers as defined with the following Kubernetes logical objects:
Kubernetes objects mapped to Pega nodes
| Node/purpose | Kubernetes replica set | Kubernetes service | Kubernetes ingress | Kubernetes ConfigMap |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Web – interactive Pega nodes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Batch – background processing Pega nodes | yes | yes | ||
| Stream (Kafka) – customer’s data intake | yes (stateful) | yes | yes | yes |
| External Cassandra (Datastore) | yes (stateful) | yes | ||
| External Elasticsearch (deployed on dedicated Search nodes) | yes (stateful) | yes | ||
| Backing service SRS (Backing services not running Elasticsearch) | no | yes | no | |
| Backing service SRS (Backing services running Elasticsearch) | yes (stateful) | yes | no |
Previous topic About client-managed cloud Next topic Meeting requirements and prerequisites
