Optimized Storage Stream for reduced BLOB size
Valid from Pega Version 7.1.8
All clipboard pages are serialized and are stored in BLOB columns named pzPVStream in the Pega 7 database. The Storage Stream (byte stream) that is stored in these BLOB columns has been optimized to make the BLOB values smaller, and to also make the encoding and reading of these values faster when opening and saving objects.
This update was completed by reducing redundancies in the stored data, redesigning the data structure to be more space efficient, and by selectively encoding only parts of the stream, instead of encoding the entire stream on each read.
For more information, see the help topic Storage Stream.
Custom PL/Java Modules for PostgreSQL 9.3
Valid from Pega Version 7.1.8
To install Pega 7 for PostgreSQL 9.3, you must first install the version of PL/Java included in your resource kit. Follow the installation instructions located in:
.
Note that if you do not install PL/Java before you attempt to install Pega 7, then the Pega 7 installation fails.
PEGA0056 alert monitors PR_SYS_LOCKS defragmentation performance
Valid from Pega Version 7.1.8
The System-Locks class contains information about locks, and the PR_SYS_LOCKS table can now be periodically de-fragmented. Accordingly, any increase in the time taken to defragment the table associated with this class results in an increase in the time taken by a requestor to acquire or release a lock.
The PEGA0056 alert indicates that the defragmentation exceeds the time threshold that is configured in the prconfig.xml file. When the alert is triggered, you can modify the defragmentation interval or disable defragmentation.
For more information, see PEGA0056 alert: Defragmentation of the table associated with class System-Locks exceeded the configured time threshold.
PEGA0055 alert detects clock drift in a multi-node clustered environment
Valid from Pega Version 7.1.8
Clocks in most of the hardware platforms run at different rates, and the PEGA0055 alert detects the clock drift on any of the nodes in a multi-node cluster. The alert is triggered when the clock drifts from the average time of the clocks in the cluster by an amount that exceeds the time threshold configured in the prconfig.xml file. You can use a network time protocol service or daemon to correct the clocks by referring to a standard external Internet time service, for example, nist.gov.
For more information, see PEGA0055 alert: Clock drift exceeded the configured time threshold.
New default system setting for SQL queries
Valid from Pega Version 7.1.8
A prconfig system setting, reporting/useLayerCakeSchemaChanges, is now enabled by default to improve the performance of SQL queries. Additionally, this setting can also be configured to disable an optimized query as a prconfig setting.
Previously, this setting was set to false by default. Starting in this release, to set this from true to false, you must explicitly add an entry in the prconfig.xml file.
For more information, see Startup check removes custom DB triggers.
Startup check removes custom DB triggers
Valid from Pega Version 7.1.8
The process for performing updates to the pr_sys_updatescache and pr4_rule_vw tables has been restructured to increase system processing efficiency. In previous releases, database (DB) triggers were used to perform updates to these tables. These updates are now performed directly within the Pega 7 engine and the DB triggers have been eliminated.
Accordingly, Pega 7 now checks at startup for any user-created triggers that are added after installation. If any triggers of this type are found, they are automatically removed.
For related information, see Custom DB triggers are dropped during upgrade.
Call functions by using the library qualified syntax
Valid from Pega Version 7.1.8
When calling a function, in addition to the existing fully qualified and unqualified function calls, you can now use the library qualified syntax:
@LibraryName.FunctionName(arg1, arg2... argn)
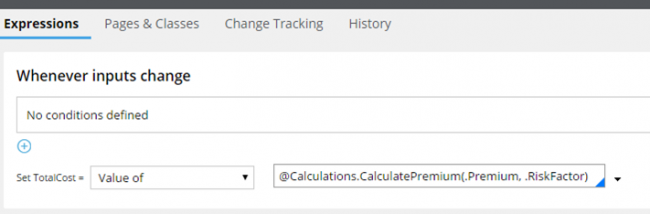
An example of using the library qualified syntax to call a function
Using library qualified notation helps prevent accidental library conflicts (such as when two libraries with the same name are located in different rulesets), because the library from the ruleset listed higher in the operator runtime ruleset list is selected for resolution.
For more information, see Methods for calling a function.
Real-time pulse processing for multinode systems
Valid from Pega Version 7.1.9
Multinode development environments now use real-time pulse processing. Previously, when a change was made on one node, the pulse processing interval could take a minute or more for that change to be reflected on another node. Now, when a rule is changed on one node, that change is immediately reflected on all the other nodes in the cluster. This change helps to ensure that users are running a rule on the same node as where the rule was changed.
Verifying that a Pega 7 Platform instance is running
Valid from Pega Version 7.1.9
You can verify whether a Pega 7 Platform instance is up and running by entering this URL: http://<<hostName:port/contextName>>/PRRestService/monitor/pingservice/ping
The Pega 7 Platform Engine responds with HTTP Response Code 200 if the instance is available. The response contains JSON text in the format { "duration":"<time in milliseconds>" }. Any other response codes or timeout indicate that the instance is unavailable.
Database storage used for passivation in High Availability mode
Valid from Pega Version 7.1.9
When an application is running in High Availability mode, the value attribute for initialization/persistrequestor/storage in the prconfig.xml file or the Dynamic System Settings now defaults to "database."
Previously, applications running in High Availability mode required shared passivation, where either initialization/persistrequestor/storage was set to “OnTimeout” or a custom passivation mechanism was used. The change to using database by default provides persistent storage for passivation, and provides control for the landing page for High Availability.
For more information, see Understanding passivation and requestor timeouts and the High Availability Administration Guide.

