Third party liability edits
Third-party liability (TPL) or Coordination of Benefits (COB) is when another insurer or program is responsible for medical costs. This entity may pay for all or part of the cost of the claim. When this occurs, the process is known as TPL or COB.
The SCE provides comprehensive analysis and editing methodologies to identify potentially liable third-party claims, properly avoid payments for services when another insurer is liable for payment and recover payments from liable third parties.
This SCE processes two types of TPL claim edits in the TPL edits module (STP):
- Subrogation edits
- COB payer edits
Subrogation edits refers to the process that an
insurance company uses to avoid payment or to seek reimbursement from the
responsible party for a claim which is associated with an accident. The SCE has
three key steps to support subrogation. The first is to identify if the claim meets
the criteria, the second is to attempt to match to an existing subrogation case and
the third is to review and resolve the claim. 
A claim is identified as a subrogation claim when one of the following criteria is met:
- For Professional or Dental Claims:
- When the Accident Indicator on the Claim is marked as
- AA - Auto Accident
- EM - Employment
- OA - Other Accident
- When the Accident Indicator on the Claim is marked as
- For Institutional Claims:
- An occurrence code is on the inclusive list
(OccurrenceCodeInclusiveList) decision table. This table can
be extended as necessary to add other applicable codes or settings:
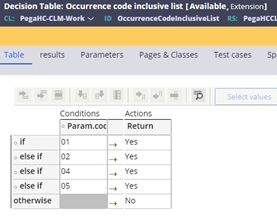
- An occurrence code is on the inclusive list
(OccurrenceCodeInclusiveList) decision table. This table can
be extended as necessary to add other applicable codes or settings:
- When the diagnosis code on the claim, falls into one of the diagnosis codes on
the Inclusive Diagnosis IsAccidentInclusive decision table, and not as a
record on the Exclusive Diagnosis IsAccidentExclusive decision table.
These tables can be extended as necessary to add other applicable codes or
settings.
- The inclusive table is delivered with the following configuration:
- E section – external causes of injury (for example, E810 – E819 are motor vehicle traffic accidents, E830 water transport accidents, E990–E999 are injury resulting from operations of war).
- V codes - supplementary classification of factors influencing
health status and contact with health services.
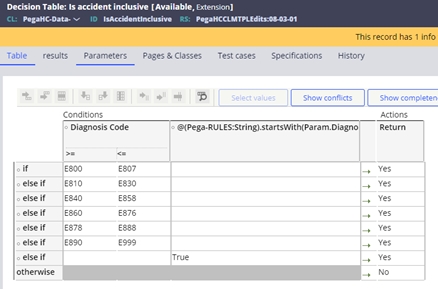
- The inclusive table is delivered with the following configuration:
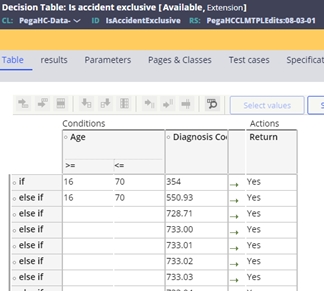
- The exclusive table is delivered with the following configuration to remove
situations where the event code will be assigned:
- 354 Carpal tunnel and if the patient is under 16 or over 70 years old
- 550.93 Hernia and if the patient is under 16 or over 70 years old
- 728.71 Plantar fascial
- 733.00-09 Osteoporosis
- 911.4 - 919.5 Insect Bite
- 935.1 Foreign body in the esophagus
- 996.62 Infection due to vascular devise
- The billed amount is more than the subrogation dollar limit on the system configuration screen.

Once the claim has identified as a subrogation claim, the appropriate event code associated with the claim type is assigned. If the claim is missing key information, for example the accident date, or occurrence code date, event codes are also set. The list of subrogation event codes is detailed below:
| Event code | Name | Description |
| STP-0015 | Missing accident date | The services billed on the claim are related to an auto or employment-related accident, but no accident date was submitted on this professional or dental claim. |
| STP-0016 | Missing occurrence code date | The occurrence code submitted on this institutional claim indicates an accident, but no date was submitted with the occurrence code. |
| STP-0017 | Subrogation - reason for visit | An accident subrogation investigation may be required based on the reason for visit code submitted on this institutional claim. |
| STP-0018 | Subrogation - external cause of injury | An accident subrogation investigation may be required based on the external cause of injury code submitted on this institutional claim. |
| STP-0019 | Subrogation - principal DX | An accident subrogation investigation may be required based on the principal diagnosis code submitted on this professional or dental claim. |
| STP-0020 | Subrogation - other DX | An accident subrogation investigation may be required based on another diagnosis code submitted on this professional or dental claim. |
| STP-0021 | Subrogation - principal DX | An accident subrogation investigation may be required based on the principal diagnosis code submitted on this institutional claim. |
| STP-0022 | Subrogation - other DX | An accident subrogation investigation may be required based on another diagnosis code submitted on this institutional claim. |
| STP-0023 | Subrogation - admitting DX | An accident subrogation investigation may be required based on the admitting diagnosis code submitted on this institutional claim. |
| STP-0024 | Subrogation - occurrence code | An accident subrogation investigation may be required based on an occurrence code submitted on this institutional claim. |
| STP-0025 | Subrogation - auto accident | An accident subrogation investigation may be required based on the auto accident indicator submitted on this professional or dental claim. |
| STP-0026 | Subrogation - employment accident | An accident subrogation investigation may be required based on the employment accident indicator submitted on this professional or dental claim. |
| STP-0027 | Subrogation - other accident | An accident subrogation investigation may be required based on the other accident indicator submitted on this professional or dental claim. |
After identifying that the claim meets the criteria for a subrogation claim, the SCE checks the member ID, principal or other diagnosis code, accident date or service date on the claim to see if there is an existing subrogation case in the system. In the instance the accident date does not exist on the claim, the subrogation case search looks for cases with an accident date of +/-60 days from the dates of service on the claim. Depending upon the search results and the status of the case, one or more of the following may occur:
- If the search does not return a case, a new subrogation case is created and linked to the subrogation claim. The case is prefixed with SB-.
Note - when the accident date is not submitted on the claim, and the claim is inferred to be subrogation through the logic defined above, the claim date of service is used as placeholder for the accident date in the subrogation case.
- If the search returns a case, then the claim is linked to the matched subrogation case.
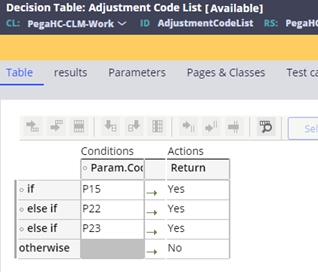
- If the claim is reported with an adjustment code indicating that the other
insurer has paid for the claim, then the subrogation case is updated to be
Resolved-Completed and the subrogation event code reported on the claim
overridden and moved to the closed event codes. The adjustment codes for
subrogation resolution are defined in the Adjustment Code List decision
table:
- If the claim matches multiple subrogation cases, event code STP-0028 is assigned:
| Event code | Name | Description |
| STP-0028 | Multiple subrogation cases | More than one subrogation case exists; the system identified claims with accident dates up to 60 days before or after the accident date submitted on this claim |
The SCE provides a guided event resolution model
(ER_ SubrogationMetaFlow) for the resolution of a subrogation event. This guided
event flow provides a series of Incident Questions (IQs) to support the resolution
of the claim. Selecting the option Accident Q & A will start the guided
process. 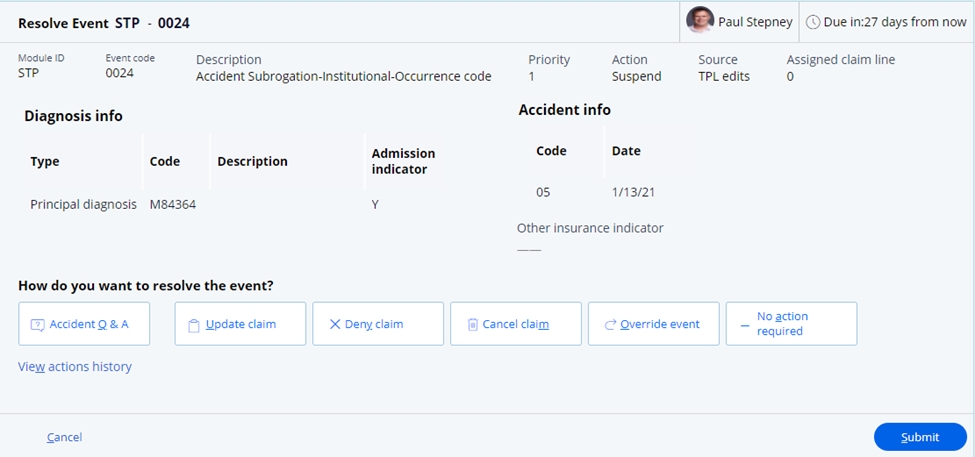
The questionnaire has a series of four steps to
get key information associated with the subrogation case. 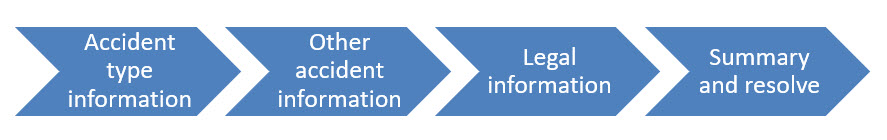
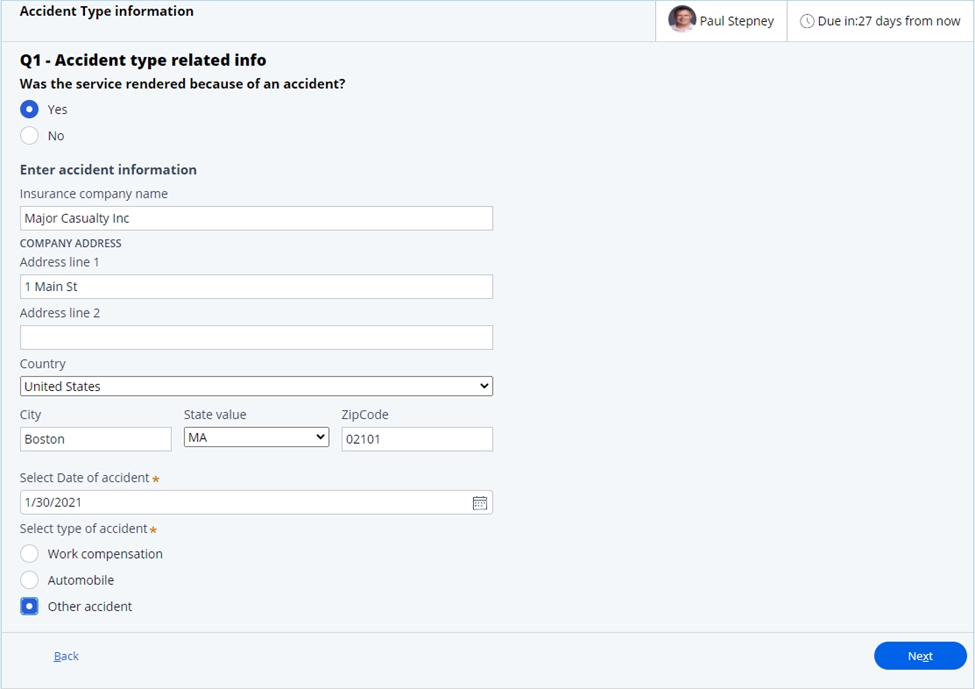
- Accident type information. In this step, if the services were not
rendered as part of an accident, the user would be taken to the last step of the
questionnaire. If the services were due to an accident, key information relating
to the insurance company and the accident date and type can be entered.
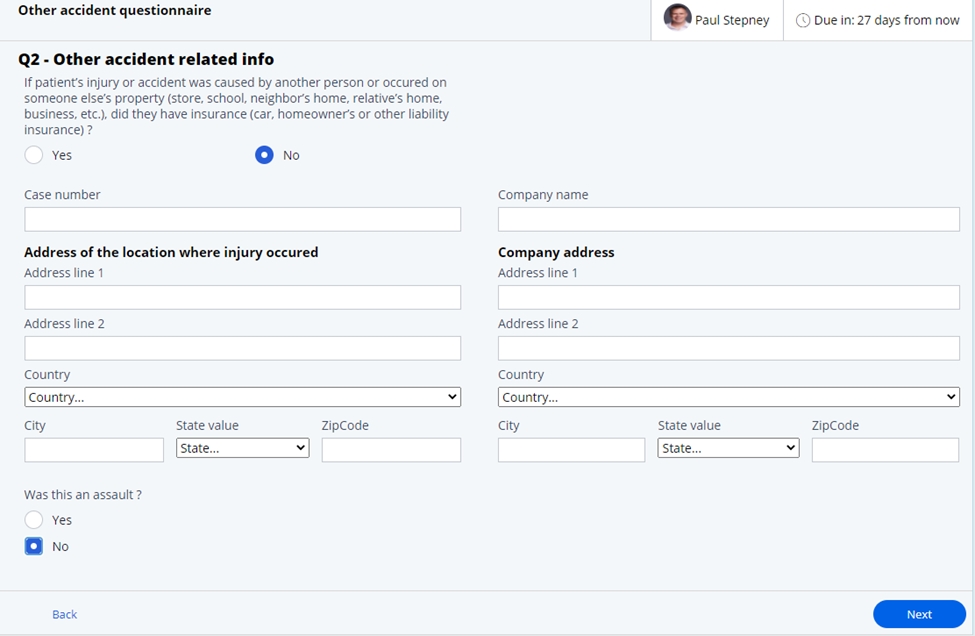
- Other accident related info. In this stage, if there is another party at
fault, information relating to the location of the accident and the other
insurance company can be entered.
- Legal information – If a lawyer has been retained to support any
litigation, this information can be entered, along with any settlement
information once completed.
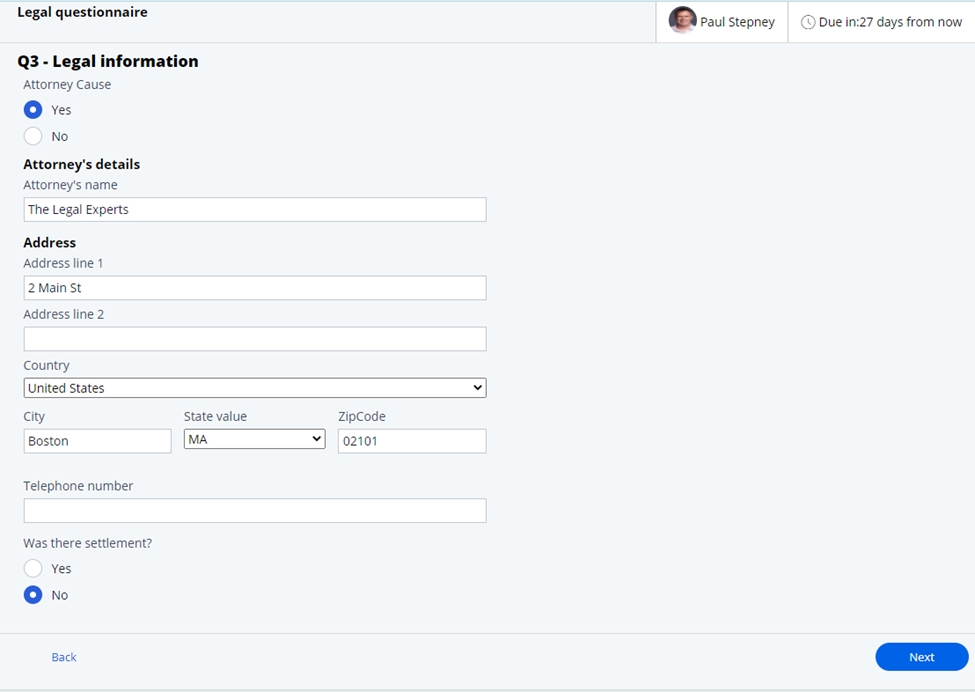
- Review and resolve – In this step, the user can review information
entered during any other step in the process and if needed, update the
information.
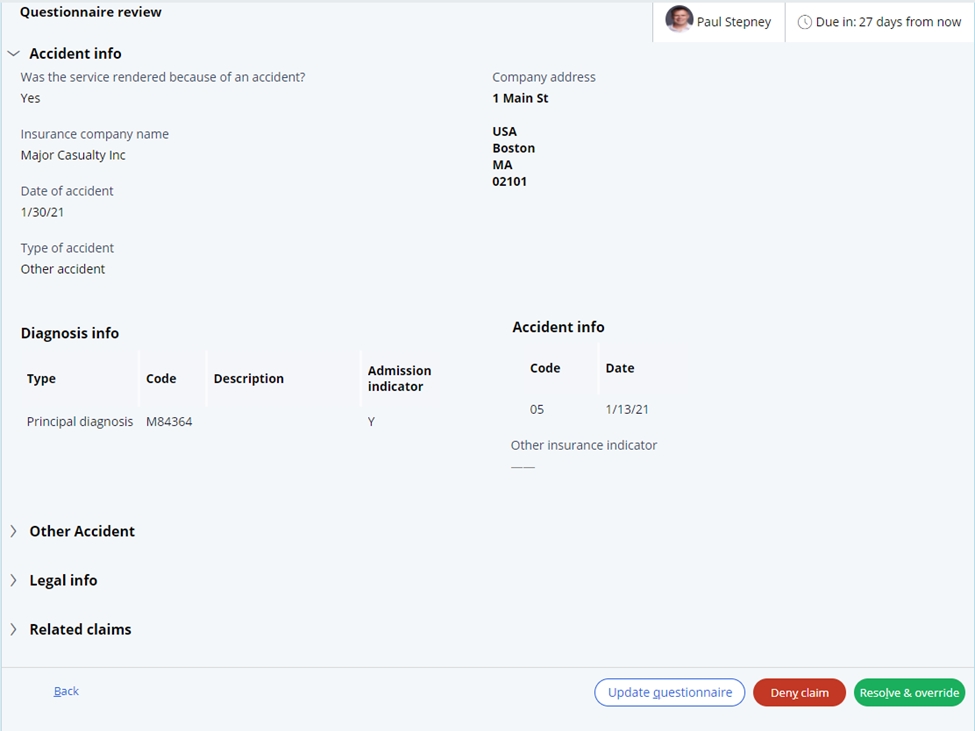
The related claims will provide a link to the claims associated with this subrogation case.
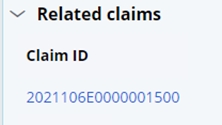
At this step, the user is presented with two resolution options.
A. Deny the claim. In this instance, the current claim will be denied. This will keep the subrogation case open for future claims to be applied.
B. Resolve and override. In this instance, the event code will be overridden so that the claim can adjudicate, and the subrogation case will be resolved.
COB payer editsThird Party Liability, also known as coordination of benefits (COB), is a claim adjudication process that identifies if parties other than the system’s insurance company have a level of financial responsibility for a submitted claim. Additional third-party liability or coordination of benefit information is supplied as part of the patient match through the membership module. The policy information for the member is stored in the membership data model and ordered based on the ranking that is detailed in the chapter on Member Matching and provided through the eligibility and policy module (SMP).
The SCE checks if COB information is submitted on the claim to show other coverage and how much was paid. The SCE then identifies whether this information is used in the adjudication of the claim, or whether the claim should set an event code, for further review against the other insurer.
The following are examples of the four types of logic used to set COB event codes by the system:
- The SCE identifies that the member has external insurance that is ranked higher than the payer policy, but the claim does not contain payment information in the COB sections from that other insurer.
- The SCE does not recognize the COB information submitted on the claim with the member in the membership system.
- The other insurer paid zero, but the associated adjustment information indicating why they paid zero is not valid.
- The SCE identifies that the claim meets criteria for another payer to pay first.
The SCE uses information on the member record to indicate that an active external payer exists. The claim list then reviewed to see if the other payer payment information has been submitted with the claim. If the claim does not contain the other payer information, the event code STP-0001 will be assigned on the claim.
Unknown, inconsistent, or invalid other insurance information submittedThe SCE reviews the COB information submitted on the claim to validate that the other insurer is known in the system and that the information submitted is correct.
If the other payer information is unknown to the SCE, then either event code STP-0007 is assigned or STP-0008 is assigned to the claim. STP-0007 indicates that the other subscriber was not found and STP-0008 indicates that the subscriber was found, but the policy was not located. If the other insurance subscriber submitted matched multiple records, then STP-0014 is assigned.
If the other subscriber and policy is located, then the information returned from the member system is validated against the other insurance information and member information on the claim and the following event codes may be reported:
- If the contract is not found, event code STP-0010 is assigned.
- If the subscriber name differs, event code STP-0005 is assigned.
- If the subscriber address differs, event code STP-0006 is assigned.
- If the other payer name is blank, event code STP-0003 is assigned.
- If the other payer name is not found, event code STP-0011 is assigned.
- If the other payer name differs, event code STP-0012 is assigned.
- If the other payer paid amount is blank, event code STP-0002 is assigned.
The SCE validates the other payment amount, and in some situations, a payment of zero is not permitted. The SCE uses a decision table to review the other payer adjustments to validate if the reason for the zero payment supports a valid business scenario. For example, a payer could refuse to pay secondary on the claim if the primary payer denied the claim as the services were not authorized.
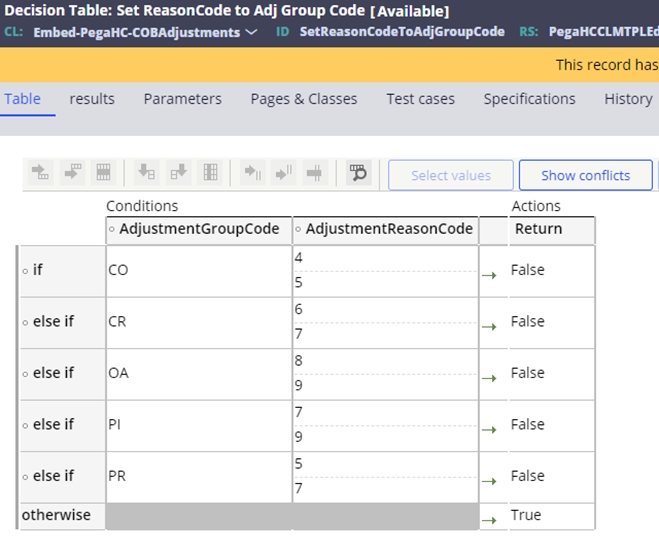
The decision table SetReasonCodeToAdjGroupCode provides the configuration for appropriate adjustments to pay zero. If the combination of the adjustment group and reason code returns false, then the claim will be valid. If not, and true is returned, then event code STP-0013 will be assigned to the claim.
 Identifying
other insurance should pay
Identifying
other insurance should payThe SCE uses a determine claim priority matrix to identify if the claim meets the criteria for another insurer to pay. Once the priority is known, and if the other payer should be billed first, the SCE reviews the submitted other insurance information to ensure of the match. If the appropriate payer and policy are identified on the claim, then the claim will process
The
priority matrix to manage the coordination of benefits (COB) is provided through the
CE_DetermineClaimPriority decision table. This is used to identify the
order of priorities for this claim. Each row on this table is configured with a when
statement to see if the conditions for that policy type exist. Samplewhen statements
are delivered with the SCE and can be extended by the clients and configured into
the priority order as needed. If the claim doesn’t match to a condition and returns
None, event code STP-0004 is applied to the claim. 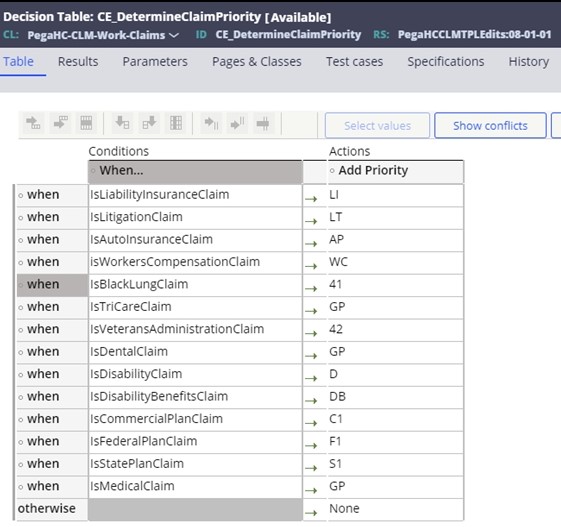
Sample when statements are detailed below:
- IsLiabilityInsuranceClaim – Checks for Accident Indicator or OA in related causes codes.
- IsAutoInsuranceClaim – Checks for Auto Accident Indicator or AA in related causes codes.
- IsWorkersCompensationClaim – Checks for Employment Indicator or EM in related causes codes.
- IsBlackLungClaim – Checks for existence of Black lung diagnosis on CE_BlackLungDiagnosis table
- IsDentalClaim – Checks to see if the claim form type is D (Dental)
The CE_GetClaimProduct table is used to find the type of product associated with the claim. If no product is found and None is returned, event code STP-0008 is set on the claim.
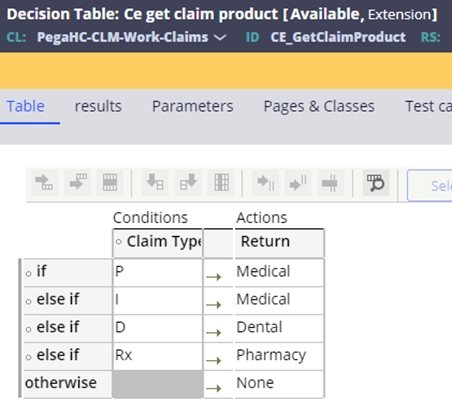
Once the order of other insurance on the claim is known, the other insurance reported on the claim is matched to the contracts, looking for a gap. If no COB is reported on the claim and no other insurance is found for that policy in the member record, event code STP-0009 will be assigned to the claim.
COB editsThe table below details the event codes that are set through the COB processing:
| Event code | Name | Description |
| STP-0001 | Missing COB info | The member record indicates that one or more other insurance policies exist, but no coordination of benefits (COB) information was submitted with the claim. |
| STP-0002 | Missing COB paid amount | The other insurance paid amount for this coordination of benefits (COB) claim is blank and the claim identifier is CH (chargeable) or RP (reporting). |
| STP-0003 | Missing COB payer name | The other insurance payer name for this coordination of benefits (COB) claim is blank and the claim identifier is CH (chargeable) or RP (reporting). |
| STP-0004 | Invalid product type | The product type submitted with the coordination of benefits (COB) information is not valid for this claim type. |
| STP-0005 | Different COB subscriber name | The other subscriber name for this coordination of benefits (COB) claim does not match the system. |
| STP-0006 | Different COB subscriber address | The other subscriber address for this coordination of benefits (COB) claim does not match the system. |
| STP-0007 | Other subscriber not found | The member ID submitted for the other subscriber on this Coordination of Benefits (COB) claim was not found in the system. |
| STP-0008 | No COB subscriber policy found | The other subscriber policy for this coordination of benefits (COB) claim is not found in the system. |
| STP-0009 | Invalid contract | The submitted policy contract type as well as the submitted other payer policy contract type (if any), are invalid for this claim. |
| STP-0010 | No COB subscriber contract found | The other subscriber contract for this coordination of benefits (COB) claim is not found in the system. |
| STP-0011 | No COB payer found | The other subscriber policy and contract for this coordination of benefits (COB) claim do not have an associated payer. |
| STP-0012 | COB payer mismatch | The other subscriber policy and contract for this coordination of benefits (COB) claim shows a different payer from what was submitted on the claim. |
| STP-0013 | COB paid zero | The other payer paid amount for this coordination of benefits (COB) claim is zero and the submitted adjustment reason code and adjustment group code indicate review is required. |
| STP-0014 | Multiple COB subscribers found | Multiple other subscribers for this coordination of benefits (COB) claim were found in the system. |
Previous topic Claim business audits Next topic Split claims
