Personas
You can manage users more intuitively through personas, which represent realistic, relatable groups of users of your application. Personas store comprehensive information about user needs and behaviors in the context of the roles that are typical to your organization.
Personas are a design tool that help you group users into convenient cohorts according to
their work objectives, tasks, needs, attitudes, skill sets, and behavior. Typically,
user personas derive from behavioral and work process research within your business
organization, and are often presented in a concise visual format to display the
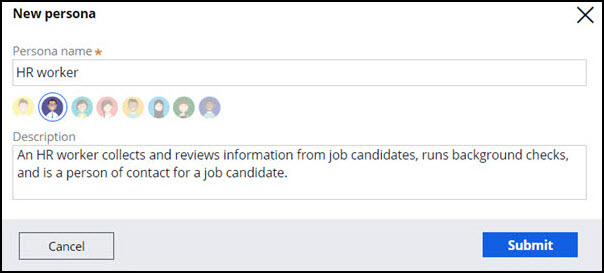
meaningful commonalities in each group. For example, the following figure depicts a
sample HR worker
persona configuration.
Personas and user roles are similar, but not the same. A user role is typically defined in terms of tasks to be done, while a persona creates a broader narrative to build user empathy, prioritize user needs, and align them to business outcomes.
For example, an auto insurance claim can include a customer persona and a Customer
Service Representative (CSR) persona. The customer is stranded on the side of the road,
trying to fill in an auto insurance claim. The CSR is taking the Customer's information
over the phone. The Customer is likely experiencing a high-stress situation with limited
access to information. Their goal is to get help as quickly as possible. The CSR working
in the application shares the goal of assisting the Customer, but must also obtain
accurate information to begin the claim process. The CSR is also in a different
emotional state. While both personas share the main objective of filing a claim, their
attitudes, demands, skill sets, and feelings are different and require different
in-product experiences.
| Persona | Location | What are they doing? | Goal | Access to information |
| Customer | Side of the road | Calling for help | Get help quickly | Limited |
| CSR | Office | Taking the call | Provide help quickly | Good |
Understanding personas helps you gain a more granular level of control over the user experience, from defining which stages of a case belong to which type of user, to customizing the interface to include only the information that a specific role requires. You can create as many personas as you like, and use them as reference for building access groups in your application.
Previous topic Future-proof UI design Next topic Major differences between traditional UI and Theme Cosmos components
