Configuring ethical bias checks
You can test your strategies for unwanted bias by creating an ethical bias policy. For example, you can test whether your strategies generate biased results by sending more actions to male rather than female customers, as well as check how big the bias is. Perform the following procedure to configure the fields that you want to use to measure bias, and to define the thresholds for detecting bias.
- In the Pega Customer Decision Hub portal, click
- On the Bias fields tab, click Add bias
field.
- If the property that you select has a number value, in the Add bias
field window, specify whether you want Pega Platform to interpret the value as a category (for example,
gender or ethnicity), or as an ordinal number (for example, for age).
- On the Bias fields tab, review and configure the bias
threshold settings for each issue in your business structure.The bias threshold measurement depends on the type of field that you select:
- Rate ratio - Rate ratio is used to calculate bias for
categorical fields by comparing the number of customers who were
selected for an action to those not selected for an action, and then
correlating the result to the selected bias field. For example, the rate
ratio represented in the following table indicates that actions are sent
more often to male rather than female customers:
Female customers Male customers selected for the action 500 1000 not selected for the action 20000 18000 rate ratio 0.46 2.16 Bias threshold Allowed rate ratio range no bias allowed any bias with a 95% confidence for the rate ratio being greater than or less than 1 will be detected very light 0.9-1.11 light 0.8-1.25 heavy 0.66-1.50 very heavy 0.5-2.0 all bias allowed no bias detection For the rate ratio, the confidence interval is calculated using the approximation on the error on log on.
Bias threshold values and allowed rate ratio range 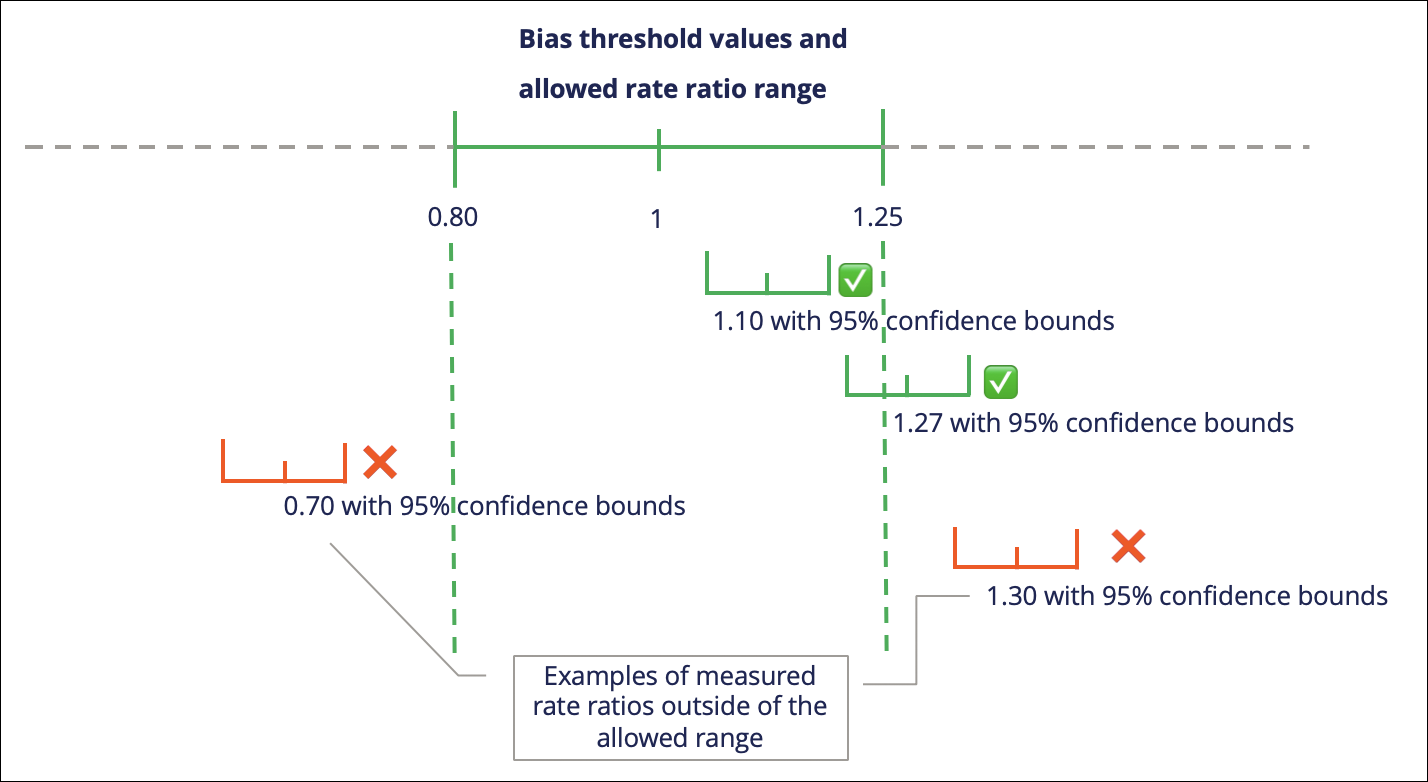
- Gini coefficient - The Gini inequality coefficient is used
to calculate bias for numerical fields. For example, it detects whether
the distribution of age is different for customers who receive an
action. A Gini coefficient of 0 represents no shifts in the
distribution. You can select a warning threshold between
0 (send a warning if any bias is detected)
and 0.50 - 2.00 (send a warning only if very high
bias is detected). If the measured Gini coefficient is outside of the
allowed range with a confidence interval of 95%, it will signify a
significant bias. You can also choose to ignore this bias field for a
particular issue in your business structure.
Bias threshold Allowed Gini range very light < 0.1 very light < 0.2 heavy < 0.5 very heavy < 0.7 no bias allowed any bias with a 95% confidence for the Gini coefficient to be greater than 0 will be detected all bias allowed no bias detection The confidence interval for the Gini coefficient is calculated using Delong's method.
- Rate ratio - Rate ratio is used to calculate bias for
categorical fields by comparing the number of customers who were
selected for an action to those not selected for an action, and then
correlating the result to the selected bias field. For example, the rate
ratio represented in the following table indicates that actions are sent
more often to male rather than female customers:
- Click Save.
- To use the bias policy to test the behavior of your strategies:
- In the Pega Customer Decision Hub portal, click Simulation Testing.
- Create a new simulation test with the purpose Ethical
bias.For more information, see Running a decision strategy simulation on sampled production data.
Previous topic Using Geofences in strategies Next topic Supplementing next-best-action with traditional outbound campaigns
